Reducing the impact on our world
At Venator, we take responsibility for our environmental footprint and are committed to reducing emissions, minimizing waste, and driving sustainable manufacturing. Our products play an essential role in modern life, and with that comes the duty to operate responsibly and support our customers in meeting their own sustainability goals.
All operational manufacturing sites are certified to ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, with environmental performance overseen by on-site EHS managers who drive continuous improvement in areas such as energy, emissions, water, and waste. Our goal to reduce scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 50% by 2030 remains central to our Planet agenda, supported by accurate measurement, energy efficiency, and circular economy principles. The launch of our V-PCF product carbon footprint tool marks a step forward in enabling data-led decisions that reduce both carbon and waste, for Venator and for our customers.
Emissions and energy management
We recognize our responsibility to minimize our environmental impact by tackling climate change and the GHG emissions we produce throughout our value chain. Our operations are energy-intensive, and with our vast value chain, we are consistently looking for ways to reduce our direct GHG emissions footprint. We look to do this through energy efficiency improvements, energy infrastructure transformation, and site decarbonization plans. Through this, we can strengthen our resilience and accelerate progress toward our 2030 climate goals.
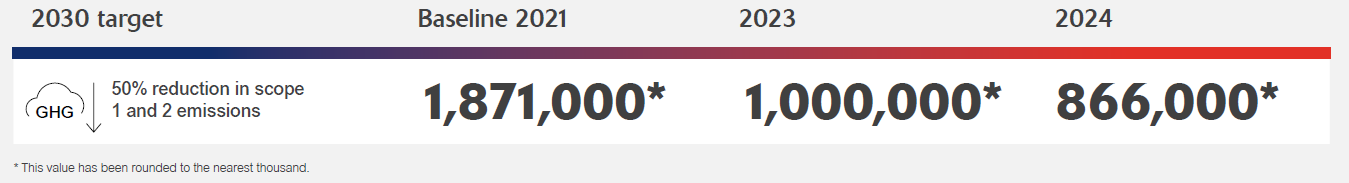
Reducing our greenhouse gas emissions: Our 2024 carbon footprint
Our decarbonization strategy remains central to achieving our 2030 target of reducing scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 50%. Since the strategy was developed in 2022, we’ve made steady progress through site-specific emissions reduction plans and energy transformation initiatives across our global operations.
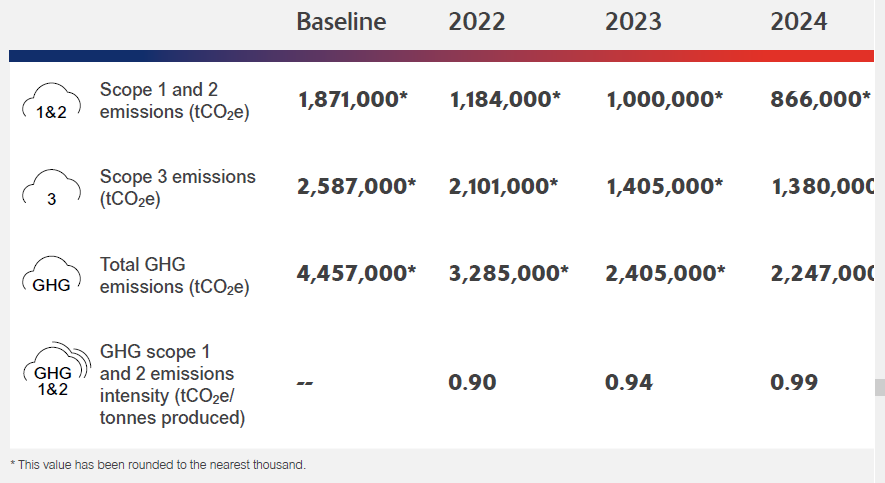
In 2024, we achieved a 13.4% reduction in absolute scope 1 and 2 emissions compared to the previous year. While part of this reduction resulted from the wind-down of operations at selected sites, we saw a marginal increase in our emissions intensity metric which increased from 0.94 to 1.00. This can be attributed to the general fluctuation in production and the business’s transition throughout 2024, particularly from an energy use perspective. Our indirect scope 2 emissions increased, driven by changes in operational demand and energy sourcing. Shifting market conditions also shaped performance, affecting energy use and production rates across the business.
In parallel, 2024 marked the first year we successfully calculated our scope 3 emissions in time for inclusion in this report, reflecting improvements in our data collection and reporting capabilities. In addition to our work to decarbonize our upstream scope 3 emissions, we recognize that there is still a proportion of emissions within our downstream, particularly with our customers processing our TiO2 into their own products. We are working to identify ways in which we can work with our customers to reduce their scope 1 and 2 emissions and consequently reduce our downstream scope 3 emissions.
Looking ahead, we will continue to advance energy reduction and emissions efficiency projects across all manufacturing sites. Each location has identified specific areas for improvement, including energy use, TiO2 yield, and raw material efficiency. These initiatives are designed to cut emissions, reduce energy costs, and help ease the demand on the grid—particularly as we increase our reliance on renewable energy sources.
Progress and Impact
Case Study: Monitoring biodiversity at Venator’s Greatham site
As part of our commitment to biodiversity, a moth survey was carried out at our Greatham site by the Industry Nature Conservation Association (INCA). Moths are valuable indicators of ecosystem health, and the findings provide a useful baseline to guide future biodiversity efforts.
Using light traps, the survey recorded 34 species, including ten uncommon in the region. Among these were species usually associated with reedbed environments, such as Webb’s wainscot, and grassland moths like the dusky sallow, both of which thrive in alkaline-rich habitats. Interestingly, these habitats have developed across the Tees estuary through historical industrial land use, showing how reclaimed land can support unique ecosystems.
The results highlight the ecological value of our site and the importance of habitats such as reedbeds and grasslands. Going forward, we will build on this work through seasonal monitoring, and use the findings to inform a Site Biodiversity Action Plan, helping us protect and enhance biodiversity as part of day-to-day site management.
Venator's Huelva facility, Spain installs electric vehicle charging stations
Promoting sustainability and adaptation to modern needs
Our Huelva facility, Spain has taken a significant step towards sustainability by installing electric vehicle charging stations at their Palos de la Frontera site. The initiative, aimed at promoting eco-friendly transportation and supporting the needs of associates and contractors, features eight charging stations for associates and four for contractors, all located at the main parking area of the site.
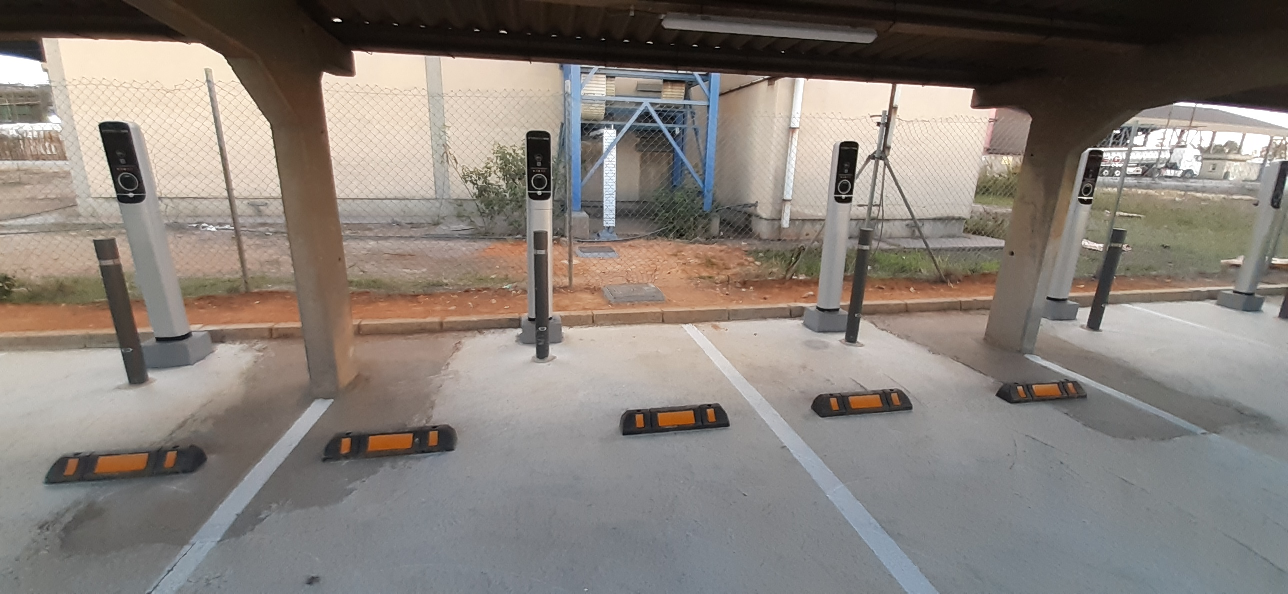

Each charging station boasts a capacity of 22 kW, ensuring efficient and rapid charging for electric vehicles. This project aligns with the legislation set forth in Royal Decree-Law 29/2021, demonstrating our commitment to compliance and modern environmental standards.
The project has been supported by MOVES III, funded with Next Generation EU funds as part of the Ministry for the Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge, and the Recovery, Transformation, and Resilience Plan.
By investing in this infrastructure, Venator P&A Spain is not only fostering a sustainable future but also addressing the evolving requirements of their workforce and contributing to the broader goal of reducing carbon emissions through the promotion of electric vehicles.